1.딕셔너리 자료형 Dictionary data type
1) 딕셔너리란? What is a Dictionary?
- 딕셔너리는 키(Key)와 값(Value)의 쌍을 저장하는 대용량의 자료구조
A dictionary is a large-capacity data structure that stores pairs of keys and values - 파이썬이 아닌 다른 언어에서도 이런 대응 관계를 가지는 자료형을 갖고 있는데, 이를 연관 배열 또는 해시라고 함
Other languages than Python also have this corresponding datatype, which is called associated arrangements or hashes - 딕셔너리의 가장 큰 특징은 리스트나 튜플처럼 순차적으로(=인덱스로) 요소를 꺼낼 수 없고 Key를 통해 Value를 얻음
The most distinctive feature of dictionaries is that elements cannot be pulled out sequentially (=indexed) like lists or tuples, and values are obtained through the key - 순차적으로 꺼내지 못하니 요소들의 순서는 의미가 없음. (=순서가 달라져도 동일한 딕셔너리.)
The order of the elements is meaningless because they cannot be taken out sequentially. (=The same dictionary even if the order is different.) - 중괄호{} 안에 Key:Value 형태를 넣고 콤마,로 구분해줌. 딕셔너리명 = {Key1:Value1, Key2:Value2, Key3:Value3, ...}
Put the Key:Value form in brackets {} and separate it with comma.
Dictionary name = {Key1:Value1,Key2:Value2,Key3:Value3,...} - 키(Key)는 중복되면 안 되고, 값(Value)은 중복되어도 상관 없음
The key should not be duplicated, and the value may be duplicated
# 중괄호{} 안에 Key:Value 형태를 넣고 콤마,로 구분
Key:Value in brackets {} separated by comma
# 순서가 달라져도 동일한 딕셔너리
# Same dictionary even if the element order is different
dic = {'apple':'사과', 'orange':'오렌지', 'melon':'멜론', 'num':8}
dic
>>>{'apple':'사과', 'orange':'오렌지', 'melon':'멜론', 'num':8}
# 키(Key)는 중복되면 안 되고, 값(Value)은 중복되어도 상관 없음
# The key should not be duplicated, and the value may be duplicated
# 중복되는 키가 있을 때 확인해보기
# Check when duplicate keys exist
dic = {'apple':'사과', 'orange':'오렌지', 'melon':'멜론', \
'num':8, 'apple':'꿀사과', 'num_2':8}
dic
>>>{'apple': '꿀사과', 'orange': '오렌지', 'melon': '멜론', 'num': 8, 'num_2': 8}중복되는 key가 있으면 하나를 제외한 나머지 것들이 모두 무시
If there is a duplicate key, ignore everything except one
2) 딕셔너리 쌍 추가, 삭제, 수정 Add, delete, modify dictionary pairs
2.1. 딕셔너리 쌍 추가하기 Adding dictionary pairs
# 새로운 키에 값을 할당하면 딕셔너리 쌍이 추가
# Assigning a value to a new key adds a dictionary pair
a = {1:10, 2:20}
a[3] = 30
a
>>>{1:10, 2:20, 3:30}
# value에 리스트도 할당할 수 있음
# You can also assign a list to value
a = {1:10, 2:20}
a['list'] = [10, 20, 30]
a
>>>{1: 10, 2: 20, 3: 30, 'list': [10, 20, 30]}
2.2. 딕셔너리 쌍 삭제하기 Delete dictionary pairs
# 예약어 del을 활용해서 요소를 삭제
# Delete an element using the reserved word del
a = {1: 10, 2: 20, 3: 30, 'list': [10, 20, 30]}
del a[1]
a
>>>{2: 20, 3: 30, 'list': [10, 20, 30]}2.3. 딕셔너리 쌍에서 value 수정하기
# 변경하고 싶은 key에 새로운 값을 할당
# Assign a new value to the key you want to change
a = {2: 20, 3: 30, 'list': [10, 20, 30]}
a['list'] = [100, 200, 300]
a
>>>{2: 20, 3: 30, 'list': [100, 200, 300]}
3) 딕셔너리를 사용하는 방법 How to use dictionary
# 딕셔너리에서 key를 사용해서 value 얻을 수 있음 (리스트, 튜플과의 차별점)
# Value can be obtained using key in dictionary (different from list, tuples)
cat = {'name':'꼬미', 'breed':'모름', 'color':'gray'}
cat['name']
>>>'꼬미'
# 리스트, 튜플처럼 인덱싱 방법을 적용할 수 없음
# Indexing methods cannot be applied like lists or tuples
cat[1]
>>>
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
KeyError Traceback (most recent call last)
/tmp/ipykernel_13/2858958636.py in <module>
----> 1 cat[1]
KeyError: 1
2. 딕셔너리 관련 함수 dictionary-related functions
딕셔너리 함수 & 예약어 Dictionary Functions & Reservations
- keys() : Key 리스트 만들기 Creating a key list
- values() : Value 리스트 만들기 Creating a value list
- items() : Key : Value 쌍 얻기 Get Value Pair
- clear() : Key : Value 쌍 모두 지우기 Clear all value pairs
- get() : Key로 Value 얻기 Get Value with Key
- in : 해당 Key가 딕셔너리 안에 있는지 조사하기 Determine if the key is in the dictionary
#keys()
cat = {'name':'꼬미', 'breed':모름', 'color':'gray'}
cat.keys()
>>>dict_keys(['name', 'breed', 'color'])
# values()
cat = {'name':'꼬미', 'breed':모름', 'color':'gray'}
cat.keys()
>>>dict_values(['꼬미', '모름', 'gray'])
# items()
cat = {'name':'꼬미', 'breed':모름', 'color':'gray'}
cat.keys()
>>>dict_items([('name', '꼬미'), ('breed', '모름'), ('color', 'gray')])
# clear()
cat = {'name':'꼬미', 'breed':모름', 'color':'gray'}
cat.clear()
>>>{}딕셔너리 쌍이 모두 지워졌다 = 빈 딕셔너리가 됐다 ≠ 딕셔너리가 없어졌다. (혼동 주의)
All dictionary pairs have been erased = It became an empty dictionary
≠ The dictionary is gone (Caution of confusion)
# get
cat = {'name':'꼬미', 'breed':모름', 'color':'gray'}
cat.get()
>>>'꼬미'cat.get('name') 와 cat['name'] 은 동일한 결과값을 냄
cat.get('name') and cat['name'] give the same output
# in (key만 확인 가능)
# in (key only)
cat = {'name':'꼬미', 'breed':모름', 'color':'gray'}
'name' in cat
>>>True
# value를 넣을 경우 (잘못된 경우임)
# If value is added (incorrect)
cat = {'name':'꼬미', 'breed':모름', 'color':'gray'}
'꼬미' in cat
>>>False
3.집합 자료형 Set data type
- 수학 시간에 배운 집합과 같은 집합
the same set as the one learned in math class - 어떤 값들의 모임일 뿐 순서는 없음 (=순서가 달라져도 동일한 집합이다.)
It is only a collection of values and there is no order (=the same set even if the order is different) - 중괄호{} 안에 value를 넣고 콤마,로 구분해줌. 집합명 = {value1, value2, value3, ...}
Place value in brackets {} and separate by comma. Group name = {value1, value2, value3,...} - set() 괄호 안에 리스트나 문자열을 입력해서 만들 수도 있음
You can also create a list or string in set() parentheses - 집합은 값을 포함하고 있느냐 아니냐만 중요하고, 중복은 허락하지 않으며 순서도 별 의미 없음
Sets are important whether or not they contain values, do not allow duplication, and do not mean much in order
# 중괄호{} 안에 value를 넣고 콤마,로 구분
# Place value in brackets {} and separate by comma
# 중복은 허락되지 않음
# Duplicates not allowed
asia = {'korea', 'china', 'japan', 'korea'}
asia
>>>{'china', 'japan', 'korea'}중복을 허용하지 않는 특징을 활용해서 중복 제거하기위한 필터 역할로 종종 사용
Often used as a filter to take advantage of features that do not allow redundancy
3.1. set() 활용 Utilize set()
# 빈 집합 만들기
# Create an empty set
a = set()
a
>>>set()
# 빈 딕셔너리와 혼동을 주의
# Be careful of confusion with empty dictionaries
a = {}
type(a)
>>>dict# 리스트 넣어보기
# Putting in the list
a = set([1, 2, 3])
a
>>>{1, 2, 3}
# 튜플 넣어보기
# Putting in the tuple
a = set((11, 13, 15))
a
>>>{11, 13, 15}
# 딕셔너리 넣어보기
# Putting in the dictionary
a = set({'name':'꼬미', 'breed':모름', 'color':'gray'})
a
>>>{'breed', 'color', 'name'}key만 집합의 요소가 되어 나옴
Only the key becomes an element of the set if only the dictionary is inserted
3.2. 집합 연산 Set Operation

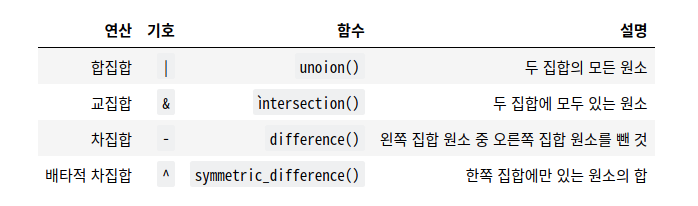
# 합집합 (a|b)
# union (a|b)
a = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12} # 2의 배수
b = {3, 6, 9, 12, 15} # 3의 배수
a.union(b)
>>>{2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12, 15}
#교집합 (a&b)
# intersection (a&b)
a = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12} # 2의 배수
b = {3, 6, 9, 12, 15} # 3의 배수
a.intersection(b)
>>>{6, 12}# 차집합 (a-b)
Relative Complement (=Difference) (a-b)
a = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12} # 2의 배수
b = {3, 6, 9, 12, 15} # 3의 배수
a.difference(b)
>>>{2, 4, 8, 10}
# 배타적 차집합 (a^b)
# Symmetric difference (a^b)
a = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12} # 2의 배수
b = {3, 6, 9, 12, 15} # 3의 배수
a.symmetric_difference(b)
>>>{2, 3, 4, 8, 9, 10, 15}
3.3. 집합 관련 함수 Set-related functions
- add() : 원소 한 개 추가하기 adding an element
- update() : 원소 여러 개 추가하기 adding multiple elements
- remove() : 특정 값 한 개 제거하기 to remove one particular value
# add()
a = {1, 2, 3}
a.add('넷')
a
>>>{1, 2, 3, '넷'}
# update()
a = set([6, 5, 4])
a.update({1, 3, 2})
a
>>>{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
# remove()
a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
a.remove(2)
a
>>>{1, 3, 4, 5, 6}
4.불(bool) 자료형 Bool data type
1) 불(bool)이란? What is bool?
- 불(bool) 자료형은 참(True)와 거짓(False) 딱 두 가지 상태만을 표현하는 타입
The bool data type is a type that expresses only two states: true and false - True, False의 첫 자가 대문자임을 유의 (true, false 소문자로 적으면 불 자료형이 아님)
Note that the first letter of True, False is a capital letter
(True, false If written in lowercase, it is not a bool data type) - 조건문의 반환 값으로도 사용됨
Also used as return value of condition statement
# type 확인
# check type
a = True
type(a)
>>>bool따옴표로 감싸지 않은 문자열을 변수에 할당해서 오류가 발생할 것 같지만 불 자료형으로 인식하기 때문에 잘 실행됨
It seems like an error might occur because we assign unquoted strings to variables, but in fact, it runs well because it is perceived as bool data type
# 소문자로 작성하였을 경우
# When written in lowercase letters
b = true
type(b)
>>>
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
NameError Traceback (most recent call last)
/tmp/ipykernel_13/2015354282.py in <module>
----> 1 b = true
2 type(b)
NameError: name 'true' is not defined
# 조건문
# conditional statement
5>4
>>>True
2) 자료형의 참과 거짓 The true and false data types
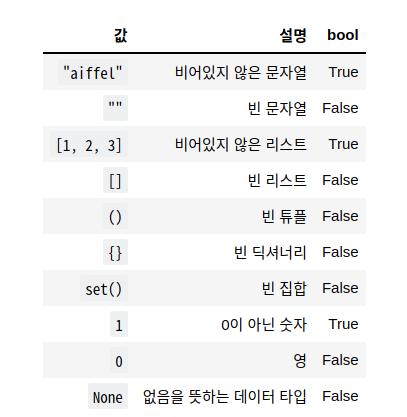
- 불 타입을 확인할 때는 bool() 함수를 이용해서 할 수 있음
You can use the bool() function to check the fire type
# 자료형 불 타입 확인해보기
# Check the bool type
bool(0.0)
>>>False
✔️ 더 알아보기 Learn more
지금까지 알아보았던 자료형과 함수 및 연산자들을 파이썬 공식 문서에서도 확인이 가능
Data types, functions, and operators that we've identified so far can also be found in Python official documents
5.변수 Variable
1) 변수란? What is Variable?
- 변수를 만들 때는 =(assignment) 기호를 사용 (변수명 = 변수에 저장할 값)
Use the = symbol when creating a variable (variable name = the value to be stored in the variable)
# 변수명 = 변수에 저장할 값
# Variable name = the value to be stored in the variable
my phone = 'iphone'
2) 변수명의 규칙 Variable Name Rule
- 영문자(대, 소문자 구분), 숫자, 언더바(_)만 사용 가능
Only English characters (case sensitive), numbers, and underbars (_) are available - 첫 자리에는 숫자를 사용할 수 없음
Number not allowed for first digit - 예약어(파이썬 키워드)는 변수명으로 사용할 수 없음
Reservation word (Python keyword) cannot be used as variable name
# 영문자(대, 소문자 구분), 숫자, 언더바(_)만 사용 가능
# Only English characters (case sensitive), numbers, and underbars (_) are available
List_01 = [1, 3, 5]
list_01 = [2, 4, 6]
List_01
>>>[1, 3, 5]
list_01
>>>[2, 4, 6]
# 첫 자리에는 숫자를 사용할 수 없음
# Number not allowed for first digit
00dic = {1:11, 2:22}
00dic
>>>File "/tmp/ipykernel_13/2595883628.py", line 3
00dic = {1:11, 2:22}
^
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
# 예약어(파이썬 키워드)는 변수명으로 사용할 수 없음
# Reservation word (Python keyword) cannot be used as variable name
True = set("Jaydenn")
True
>>>File "/tmp/ipykernel_13/2081339041.py", line 3
True = set("Jaydenn")
^
SyntaxError: cannot assign to True
3) 변수를 만드는 여러 가지 방법 Different ways to create variables
# 아무 괄호가 없다면 => 튜플
# If there is no parentheses => Tuple
# 튜플로 변수에 값을 할당할 수 있음
# Allows assignment of values to a workflow variable
a, b, c = 11, 22, 33
b
>>>22
# 리스트로도 가능
# Value assignment is also possible in list format
[d, e] = ['Hello', 'world']
d
>>>'Hello'
# 여러 개의 변수에 같은 값을 할당
# Assign the same value to multiple variables
f = g = True
f
>>>True
# 위와 같이 여러 개 변수 값에 같은 값 할당의 원리로 두 변수의 값 변경 가능
# As above, you can change the values of two variables by assigning the same value to multiple variable values
a = 'Hello, python world'
b = 10
a, b = b, a
a, b
>>>(10, 'Hello, python world')
'Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Python] Loop (0) | 2023.10.04 |
|---|---|
| [Python] Conditional statement (1) | 2023.10.03 |
| [Python] Data type (2) (0) | 2023.09.26 |
| [Python] Data type (1) (0) | 2023.09.22 |
| [Python] Basics and Terms (0) | 2023.09.21 |



