1.연산자 Operator
1) 비교 연산자 Comparison operator
- 조건식에서는 주로 변수값을 비교하는 문장이 오며, 변수가 특정 값인지 평가
The conditional expression mainly uses statements comparing variable values, evaluate if the variable is a particular value - 비교 연산자는 두 값의 상등 여부나 대소관계를 비교
The comparison operator compares the equality or magnitude of the two values
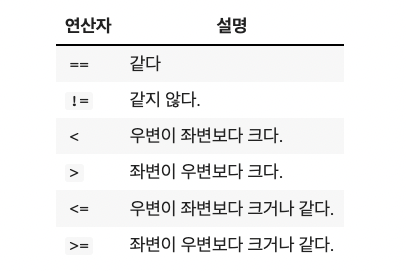
-> =기호는 대입 연산자 이고, ==는 비교 연산자
The symbol = is the substitution operator, and == is the comparison operator
-> ==는 좌변과 우변이 같으면 True를 리턴하고 다르면 False를 리턴
-> == returns True if the left and right sides are the same, and False if the other side is different
# ==
8 == 9
>>>True
# !=
8 != 9
>>>False
# =! (순서가 바뀔 경우)
8 =! 9
>>> File "/tmp/ipykernel_13/4176870740.py", line 3
8 =get_ipython().getoutput(' 9')
^
SyntaxError: cannot assign to literal
2) 논리 연산자 Logical Operators
- 두 개 이상의 조건을 점검할 때 논리 연산자를 사용
Use logical operators to check for more than one condition

# and (True and True)
3 >= 1 and 3 >= 2
>>>True
# and (True and False)
3 >= 1 and 3 >= 4
>>>False
# or (False or True)
3 >= 1 or 3 >= 4
>>>True
# not True -> False
not 3 > 1
>>>False
# not False -> True
not 3 > 5
>>>True
3) 기타 연산자 Other operators
- 기타 연산자를 활용하여 다양하게 데이터를 확인
Use other operators to check different data
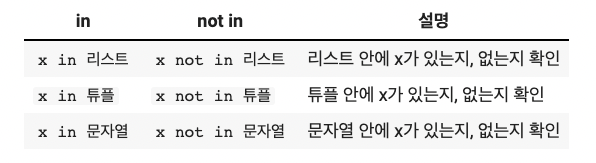
# 리스트 확인 (in)
# Check the list (in)
1 in [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] #리스트 [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] 안에 1이 있는가?
>>>True
# 리스트 확인 (not in)
# Check the list (not in)
1 not in [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] #리스트 [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] 안에 1이 없는가?
>>>False
# 튜플 확인
# Check Tuple
'd' not in ('j', 'a', 'y', 'd', 'e', 'n')
>>>False
# 문자열 확인
# Check string
'y' in 'python'
>>>True
2. if 조건문 if conditional statement
1) if문 기본 구조 if statement basic structure
- if문은 조건의 진위 여부에 따라 포함된 문장의 수행 여부를 제어
if statements control whether the included statements are performed based on the authenticity of the conditions
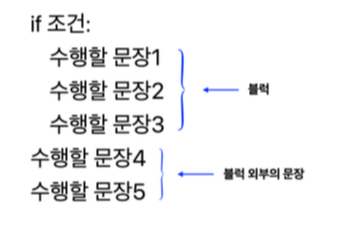
# if문 구조
# if statement structure
if 조건:
수행할 문장
조건이 참일 때 수행할 문장을 작성 (조건이 거짓이면 수행할 문장을 무시하고 지나침)
Write the statement to perform when the condition is true (ignores the statement to perform if the condition is false)
# 조건이 참일 경우
# If the condition is true
if 1:
print('조건이 참이므로 출력')
>>>조건이 참이니까 출력
#조건이 거짓일 경우
# If the condition is false
if 0:
print('과연 이건 출력이 될 것인가')조건이 거짓이므로 무시하고 지나침
Ignoring a statement because the condition is false
2) if문 블럭 구조 if statement block structure
- 조건이 참일 때, 수행할 문장이 2개 이상일 때 아래에 명령을 나열
List commands below when conditions are true and when there are more than one statement to perform
if 조건:
수행할 문장1
수행할 문장2
수행할 문장3
.
.
.
# 블럭 구조 if문 예시
# Block Structure if Statement Example
num = 10
if num > 5:
print('num이 5보다 크다')
# 블럭 구조를 제대로 지키지 않았을 경우
# If the block structure is not properly observed
num = 10
if num > 5:
print('num는')
print('5보다')
print('큽니다.')
>>> File "<tokenize>", line 5
print('5보다')
^
IndentationError: unindent does not match any outer indentation level
3) if문 예시 Example of if statement
# if문 예시
# Example of if statement
a = 7
if a == 7:
print('lucky')
>>>lucky
3. else 사용 Use else
1) else문 Else statement
- 단순한 if문은 참일때 문장을 수행하고 거짓이면 아무것도 하지 않았음
Simple if statements perform sentences when true and if false, they do nothing - else는 이와 달리 조건문이 거짓일 때 다른 문장을 수행할 수 있음
Else can perform different statements when conditional statements are false

2) else문 블럭 구조 Else statement block structure
- else문 블럭 구조는 if문과 동일.
Else statement block structure is the same as if statement.
# else문 블럭 구조
# Else statement block structure
if 조건:
수행할 문장1
수행할 문장2
else:
수행할 문장3
수행할 문장4단, if문 이후에 쓰여야 작동한다는 것만 주의
However, be careful that it works only after the if statement
3) if else문 예시 Example of an if else statement
# if else문 예시
# Example of an if else statement
score = 80
if score >= 80:
print('합격')
else:
print('불합격')
>>>합격
4. elif 사용 Use elif
1) elif문 elif statement
- if else문을 더 확장하면 elif문이 중간에 들어감
Expanding the ifse statement further puts the elif statement in the middle - if문의 조건을 만족하지 않을 때 elif문의 다른 세부 조건을 점검
Check other detailed conditions of elif statement when condition of if statement is not satisfied
if 조건_1:
수행할 문장1
수행할 문장2
elif 조건_2:
수행할 문장3
수행할 문장4
else:
수행할 문장5
수행할 문장6
구조는 다른 것과 동일하나, 순서에 유의 (if → elif → else)
The structure is the same as the others, but be aware of the order (if → elif → else)
2) elif문 예시 lif statement example
- 택시, 비용 12000원 Taxi, 12,000 won
- 버스, 1300원 Bus, 1,300 won
- 아메리카노, 비용 4000원 Americano, 4,000 won
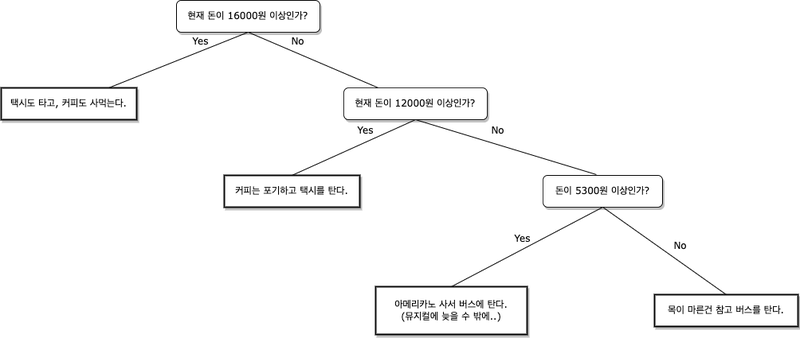
money = int(input('현재 돈이 얼마 있는가?'))
if money >= 16000:
print('택시도 타고, 커피도 사먹는다')
elif money >= 12000:
print('커피는 포기하고, 택시를 탄다')
elif money >= 5300:
print('아메리카노를 사고, 버스에 탄다')
else:
print('목이 마르지만 참고 버스만 탄다')※ input()
-> input() 함수로 사용자가 입력한 값을 변수에 저장할 수 있음.
-> The -> input() function allows you to store user-entered values in variables.
※ int()
-> int() 함수로 숫자(정수형, 실수형)나 문자열을 정수형(Integer)으로 변환할 수 있음.
-> The -> int() function allows you to convert numbers (integer, real) or strings to integer.
5. 조건문 연습 Practice conditional statements
1) if 조건문 if statement
# 자연수 x가 짝수일때만 '짝수입니다'를 출력하고 싶은 경우
# If you want to output 'even' only when the natural number x is even
x = 6
if x % 2 ==0: # x가 짝수인지 확인하는 조건
print('짝수입니다')
2) else 조건문 else statement
# 자연수 x가 짝수일 때는 '짝수입니다'를, 홀수일 때는 '홀수입니다'를 출력하고 싶은 경우
# If you want to output 'even number' when the natural number x is even, and 'odd number' when it is odd
x =5
if x % 2 == 0:
print('짝수입니다')
else:
print('홀수입니다')else 대신 x % 2 == 1를 사용해도 되지만 속도도 빠르고 메모리는 적게 차지하기 위해서 else를 사용하는 것이 더 효율적
x% 2 == 1 can be used instead of else, but using else is more efficient for faster and less memory
3) elif 사용하기 Using elif
# 자연수 x가 10의 배수인지, 2 또는 5의 배수인지, 2와 5 둘 다의 배수가 아닌지 확인하고 싶은 경우
# You want to make sure that the natural number x is a multiple of 10, a multiple of 2 or 5, and not a multiple of both 2 and 5
x = 10
if x % 10 == 0:
print('10의 배수입니다')
elif x % 2 == 0 or x % 5 == 0
print('2또는 5의 배수입니다')
else:
print('2와 5 둘 다의 배수가 아닙니다)
'Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Python] Function (0) | 2023.10.05 |
|---|---|
| [Python] Loop (0) | 2023.10.04 |
| [Python] Data type (3) (0) | 2023.09.28 |
| [Python] Data type (2) (0) | 2023.09.26 |
| [Python] Data type (1) (0) | 2023.09.22 |



