1.예약어 Reserved Words
1.1) 예약어란? What is reserved word?
- 예약어란 단어 그대로 특정 기능을 수행하도록 미리 예약되어 있는 단어를 뜻함
A reserved word literally means a word that is pre-scheduled to perform a particular function - 예약어는 절대로 변수명으로 쓰일 수 없음
Reservation word can never be used as variable name
# 파이썬의 버전 확인하기
# Check the version of Python
!python --version
>>>Python 3.9.7
# 파이썬 예약어 리스트 출력하기
# To print a list of Python reserved words
import keyword
keyword.kwlist
>>>
['False',
'None',
'True',
'__peg_parser__', # 해당 함수는 3.10버전에서 없어질 예정
'and',
'as',
'assert',
'async',
'await',
'break',
'class',
'continue',
'def',
'del',
'elif',
'else',
'except',
'finally',
'for',
'from',
'global',
'if',
'import',
'in',
'is',
'lambda',
'nonlocal',
'not',
'or',
'pass',
'raise',
'return',
'try',
'while',
'with',
'yield']
# 예약어 리스트의 개수
# Number of reserved word lists
len(keyword.kwlist)
>>>36
1.2) 25개 예약어 톺아보기 25 reserved words in depth
- 예약어 중 True, False, None 을 제외하고는 모두 소문자로 이루어져 있음 (예약어는 대,소문자를 구별하니 주의)
Except for True, False, and None of the reserved words, all are lowercase letters. (Be careful because reserved words are case sensitive.)
낯이 익은 예약어 a familiar reserved word
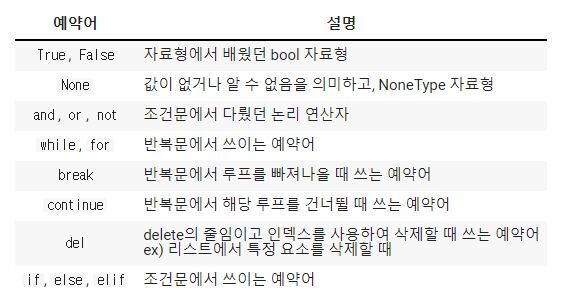
# None 데이터 타입 찍어보기
# Type None Data
type(None)
>>>NoneType
낯선 예약어 an unfamiliar reserved word
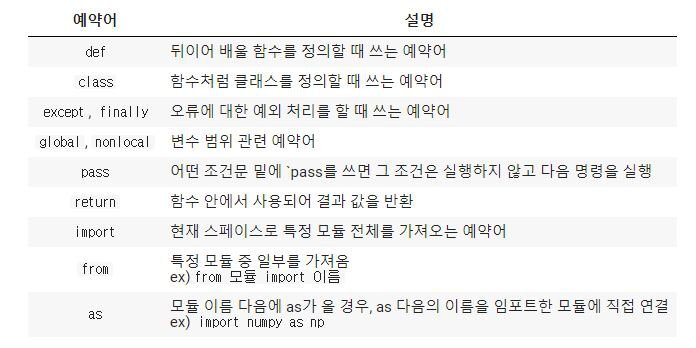
2.함수 Function
2.0) 파이썬에서 함수란? What is a function in Python?
-> 파이썬에서는 식별자 뒤에 괄호가 붙어 있으면 해당 식별자를 함수라고 부름.
In Python, if an identifier is followed by parentheses, that identifier is called a function.
-> 함수를 쓰는 이유는 프로그래밍 자체가 반복적으로 사용되는 코드 자주 쓰는데 매번 동일한 코드를 반복해서 쓰는 것보다 함수로 한번 정의해 놓고 계속 사용하는 것이 효율적이기 때문
The reason for using a function is that programming itself often uses repeated code, and it is more efficient to define it once and continue to use it rather than to write the same code over and over again each time
2.1) 함수 용어 정리 Summary of function term
함수를 만드는 것을 함수를 정의한다고 표현하고,
It describes creating a function as defining it,
정의한 함수를 사용하는 것은 함수를 호출한다고 표현함.
Using the defined function is expressed as calling the function.
함수 괄호 내부에 여러 가지 자료를 넣게 되는데, 이 자료를 매개변수(parameter) 라고 부름.
Various data are put inside the parentheses of the function, which are called parameters.
함수를 호출할 때 넣는 값을 인수(argument) 라고 부르며, 마지막으로 함수의 결과를 리턴값(return) 이라고 부름.
The value you put when you call a function is called an argument, and finally the result of the function is called a return.
2.2) 함수의 기본 구조 The basic structure of a function
- 함수는 한마디로 '코드의 집합'
A function is, in a word, a set of codes
def 함수 이름(매개변수):
수행할 문장1
수행할 문장2
...
# 간단한 함수를 만들고 톺아보기
# Create a Simple Function
def add(a, b): # 함수 이름은 add이고 입력 두개(a, b)값을 받으면
return a + b # 리턴값은 입력 두개(a, b)를 더한 값이다.
함수 이름은 add
Function name is add
매개변수는 a, b
Parameters are a, b
리턴값은 a + b 입니다.
The return value is a + b.
# 매개 변수와 인수의 차이
# Differences between parameters and arguments
def add(a, b): # a, b는 매개변수
return a + b
add(1, 2) # 1, 2는 인수매개변수는 함수에 입력된, 전달될 값을 받는 변수를 의미하고 인수는 함수를 호출할 때 전달하는 입력값을 의미
The parameter means the variable that receives the value to be passed, and the argument means the input value that is passed when the function is called
3.다양한 함수의 형태 Various forms of function
1) 입력값, 결과값이 있는 함수 Functions with input values, results
def divide (a, b):
return a//b
divide(10, 3)
>>>3
2) 입력값이 없는 함수 Function with no input value
def hello():
return 'hi!'
hello()
>>>'hi!'
3) 결과값이 없는 함수 (중요) Function without Result Value (Important)
def repeat(a, b):
print(a*b)
repeat('jayden', 3)
>>>jaydenjaydenjayden출력된 값이 있어서 결과값이 있다고 생각될 수 있지만, 결과값은 없음.
There is an output value, so it may be thought that there is a result value, but there is no result value.
결과값은 함수가 최종으로 리턴하는 값을 말하는데, 위에 출력된 값은 수행할 문장안에 있는 print함수가 실행된 것 뿐임.
The result value refers to the final return of the function, and the value output above is only the print function in the sentence to be performed.
결과값을 변수에 할당해보면 리턴값이 있는지 없는지 알 수 있음.
If you assign the result value to a variable, you can tell whether there is a return value or not.
# 변수에 함수 할당하기
# Assigning a function to a variable
check = repeat('jayden', 3)
>>>jaydenjaydenjayden
# 할당한 변수에 출력해보기
# Outputting to assigned variables
print(check)
>>>Nonerepeat함수가 호출 되어서 출력 값이 나왔지만 해당 함수를 할당한 check변수를 출력하면 None이 나오는 것을 확인
Verify that the repeat function is called and the output value is displayed, but if the check variable assigned to the function is output, None is displayed
예약어에서 언급했듯이 None은 값이 없음을 뜻 합니다. 즉, 결과값은 없음.
As mentioned in the reserved word, None means no value. That is, there is no result value.
4) 입력값도 결과값도 없는 함수 Functions with neither input nor result value
# 입력값도 결과값도 없는 함수
def repeat(): # repeat이라는 함수는
print('Hello! Python') # 'Hello! Python!' 출력한다.
repeat()
>>>Hello! Python
a = repeat()
>>>Hello! Python
print(a)
>>>None입력 인수를 받는 매개변수도 없고 return문도 없으니 입력값도 결과값도 없는 함수
Function with no parameters receiving input arguments, no return statement, no input or result value
'Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Python] Loop (0) | 2023.10.04 |
|---|---|
| [Python] Conditional statement (1) | 2023.10.03 |
| [Python] Data type (3) (0) | 2023.09.28 |
| [Python] Data type (2) (0) | 2023.09.26 |
| [Python] Data type (1) (0) | 2023.09.22 |



