1. While 반복문 While loop
1.1) while문 기본 구조 While statement basic structure
- 반복문은 유사한 명령을 계속 수행하는 제어문
A iteration recurring statement is a control statement that continues to perform similar commands
예를 들어서 1~10까지 출력하고 싶다면 아래와 같이 10번 입력해야 함
For example, if you want to output from 1 to 10, you have to type 10 times as shown below
print(1)
print(2)
print(3)
.
.
.
print(9)
print(10)
따라서 반복문은 이런 번거러움을 간단한 코드로 실현 가능
So iteration can realize this hassle in simple code
# while문의 기본 구조
# Basic structure of while statements
while 조건:
수행할 문장if문과 굉장히 유사하게 생겼고, if 키워드 대신에 while을 쓰면 됨
It looks very similar to the if statement, and you can use while instead of the if keyword
# 1부터 10까지 출력하는 코드
# Code that outputs from 1 to 10
num = 1
while 10 <= 0
print(num)
num += 1
위 코드의 알고리즘은 아래와 같으며, while은 '~동안'이라고 번역하면 됨
The algorithm of the above code is as follows, and while can be translated as '~for'
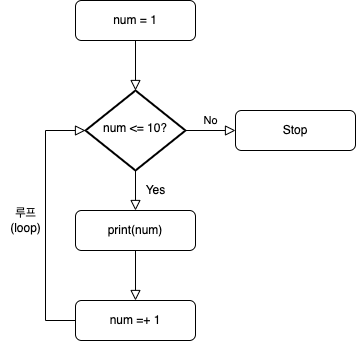
num = 1 # num은 1
while num <= 10: # num이 10보다 작거나 같을 '동안'
print(num) # num을 출력해라
num += 1 # num에 num+1 을 할당 → 루프를 타고 올라가서 while 조건 충족 여부 재확인
1.2) while문 만들고 번역하기 Create and translate a while statement
# 등차 수열의 합 while 문을 활용해서 1부터 10까지 더하는 코드 작성
# Write a code that adds the sum of the equal sequences from 1 to 10 using while loop
sum = 0
num = 1
while num 10 <= 0:
sum += num
num += 1
print(sum)
>>>55
# 위 코드 번역
# Translate the above code
num = 1 # num에 1을 할당
sum = 0 # sum에 0을 할당
while num <= 10: # num이 10보다 작을 동안
sum += num # sum은 기존 sum과 num을 더한 것이 되고,
num += 1 # num은 기존 num에 1은 더한 것이 된다.
print(sum) # while문 끝나면 sum 값을 출력
1.3) while문 강제로 빠져나가기 Forced exit from while loop
- 반복문은 조건을 만족하는 동안 반복문 안의 내용을 계속 실행
Repeated statements continue to run the content within the statement while the conditions are met - 하지만 중간에 반복을 중지하거나 현재 반복을 건너뛰어야 할 경우에 break를 사용
But if you need to stop repeating or skip the current iteration, use break
예를 들어, 꽈배기 10개를 준비한 상황에서 11번째 주문이 들어온다면 품절이라고 출력
For example, if you only have 10 twisted breadsticks and you get an order asking for 10 more, you print out that it's out of stock

# 꽈배기가 품절일 때
# When twisted bread sticks are sold out
pretzel = 10
while pretzel:
print('꽈배기', pretzel, '개 있습니다.')
order = int(input('프레젤 갯수:')
pretzel -= order
print('남은 꽈배기는', pretzel, '개 입니다')
print('*'*25)
if pretzel <= 0
print('꽈배기 품절임')
break
1.4) while문과 continue While loop and continue
- break 명령은 루프를 탈출하는 데 비해 continue 명령은 이번 루프만 건너뛰고 나머지는 계속 수행
The break command escapes the loop, while the continue command skips only this loop and continues the rest
# break
a = 0 # a는 0
while a < 10: # a가 10보다 작을 동안
a += 1 # a에 a+1의 값을 할당하고
if a % 2 ==0: # 만약 a를 2로 나눈 나머지가 0과 동일하면
break # 루프를 깨버리고 나온다.
print(a) # (if문 블럭 밖이므로) a를 출력한다.
>>>1
# continue
# continue
a = 0 # a는 0
while a < 10: # a가 10보다 작을 동안
a += 1 # a에 a+1의 값을 할당하고
if a % 2 ==0: # 만약 a를 2로 나눈 나머지가 0과 동일하면
continue # 넘어가고 루프 선두로 돌아가서 계속 루프를 탄다.
print(a) # (if문 블럭 밖이므로) a를 출력한다.
>>>
1
3
5
7
9
2. for문과 range함수 for() loop and range() function
2.1) for문의 기본 구조 Basic structure of for statements
- for문은 컬렉션의 요소를 순서대로 반복하면서 수행할 문장을 실행하는 반복
The for statement repeats the elements of the collection in order and executes the sentences to be performed - 여기서 컬렉션(collection)이란, 여러 개의 값을 모아 놓은 집합 대표적인 컬렉션은 리스트, 튜플, 문자열이 있음
Here, collection is a collection of multiple values. Representative collections include lists, tuples, and strings
# for문의 기본 구조
# Basic structure of for statements
for 변수 in 컬렉션:
수행할 문장이 때 변수는 i를 자주 씀
In this case, the variable is frequently used as i
2.2) for문 예시 Example of the for statement
- 리스트로 반복문 만들기 Create a iteration statement with a list
- 문자열로 반복문 만들기 Create a iteration statement with a string
- 다양한 for문 활용 Use a variety of for statement
# 리스트로 반복문 만들기
# Create a iteration statement with a list
a = [1, 2, 3]
for i in a:
print(i, '번 출력')
>>>
1 번 출력
2 번 출력
3 번 출력
# 문자열로 반복문 만들기
# Create a iteration statement with a string
a = 'jayden'
for i in a:
print(a)
>>>
j
a
y
d
e
n
# 다양한 for문 활용
# Use a variety of for statement
a =[('apple','사과'), ('banana', '바나나'), ('melon', '멜론')]
for (en, ko) in a:
print(en, '는(은) 한국어로', ko, '입니다.')
>>>
apple 는(은) 한국어로 사과 입니다.
banana 는(은) 한국어로 바나나 입니다.
melon 는(은) 한국어로 멜론 입니다.
2.3) for문과 continue (=for statement and continue)
- while문과 동일하게 작용
# for문과 continue 예시
# For statements and continue examples
a = [('은비', 98), ('혜린', 59), ('윈터', 72), ('닝닝', 80), ('카리나', 50)]
for (name, score) in a:
if score < 60:
continue
print(name,'님 합격을 축하합니다.')
>>>
은비 님 합격을 축하합니다.
윈터 님 합격을 축하합니다.
닝닝 님 합격을 축하합니다.
2.4) for문 + range함수 For statement + range function
- for문은 range함수와 정말 자주 쓰임 (range함수를 이용해서 간단하게 숫자들의 컬렉션을 만들 수 있기 때문)
The for statement is really often used with the range function (because you can simply create a collection of numbers using the range function) - range(시작 값, 끝 값+1, 증가 값)의 형태로 사용 (시작 값과 증가값은 생략 가능하고 그 값은 각각 자동으로 0, 1)
Use in the form of range (start value, end value +1, increase value) (start value and increase value can be omitted, and the value is automatically 0, 1, respectively)
# 예시
# an example
for i in range (0, 6, 2)
print(i)
>>>
0
2
4
# 증가 값 생략
# Omitting increment value
for i in range (0,6)
print(i)
>>>
0
1
2
3
4
5
# 증가 값, 시작 값 생략
# Increase value, skip start value
for i in range(6):
print(i)
>>>
0
1
2
3
4
5
# 음수인 증가값과 함께 쓰면 역순으로도 가능
# If you use it with negative increments, you can do it in reverse order
for i in range(6,0,-1):
print(i)
>>>
6
5
4
3
2
1
# 0까지 출력하고 싶다면 '0-1' 값을 넣어주면 됨
# If you want to output up to 0, you can add the value of '0-1'
for i in range(6,-1,-2):
print(i)
>>>
6
4
2
0
range함수를 통해서 번거롭게 리스트를 만들지 않고 다양한 숫자의 집합을 만들 수 있음
The range function allows you to create different sets of numbers without cumbersome lists
'Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Python] Function (0) | 2023.10.05 |
|---|---|
| [Python] Conditional statement (1) | 2023.10.03 |
| [Python] Data type (3) (0) | 2023.09.28 |
| [Python] Data type (2) (0) | 2023.09.26 |
| [Python] Data type (1) (0) | 2023.09.22 |



